Sidechain vs Mainchain: Understanding How They Work in Blockchain

Most people think all blockchains are built the identical, but that isn’t true. Some struggle with traffic and sluggish transactions, while others are designed to handle thousands of operations rapidly. A sidechain solves this difficulty by speeding up certain transactions, and this keeps the main blockchain running smoothly. In this article, we will explain what a sidechain and mainchain are, their key differences, and how they assist the scale and work quicker.
Key Takeaways
• A sidechain is a separate blockchain that runs alongside the main blockchain, known as the mainchain.
• These auxiliary chains allow for quicker transactions and testing new features without affecting the mainchain.
• They assist improve blockchain scalability and efficiency.
• Understanding how sidechains and mainchains interact is significant for anyone who wants to know more about blockchain projects.
What Is a Sidechain?
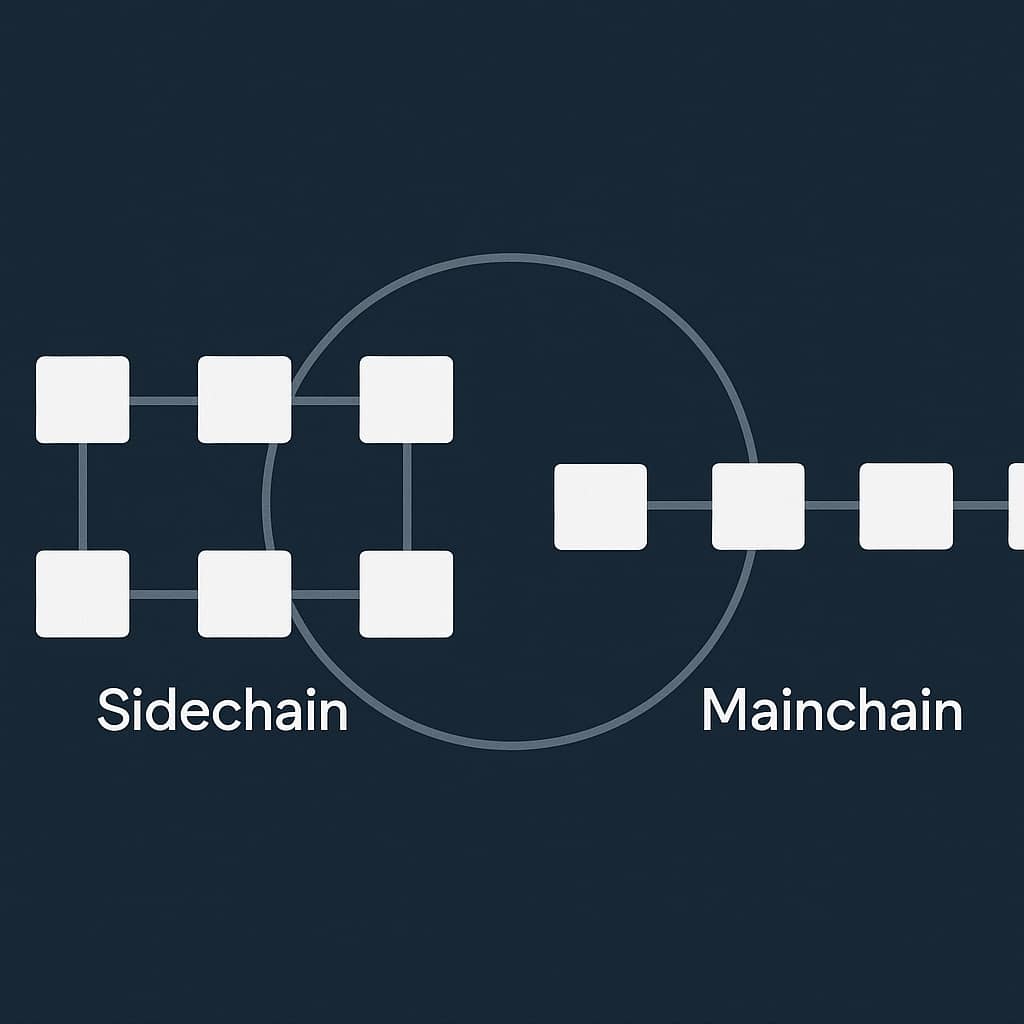
A sidechain is a blockchain that runs independently but stays connected to the main blockchain. This link allows assets to move securely between the two networks. This auxiliary chain is more like a parallel system that assists the by taking on specific tasks and transactions.
Sidechains are especially useful for testing new features, running decentralized applications, or handling transactions that don’t require the full security of the mainchain. They also assist improve speed and reduce congestion on the main blockchain. For example, a developer might use a sidechain to try out a new cryptocurrency feature before introducing it on the mainchain. A case study is the Liquid Network which is a sidechain for and is designed for quicker transactions between platforms. ETH also supports these auxiliary chains for decentralized applications that need quicker transaction processing without congesting the main ETH network.
What is a Mainchain?
The mainchain is the central blockchain where all essential transactions are recorded. It is highly secure and fully decentralized, making it the backbone of the network. The mainchain focuses on maintaining security and immutability rather than speed. This is why sidechains are useful, as they can handle experimental features and high-volume transactions without sluggishing down the mainchain.
Key Differences between a Sidechain and Mainchain
There are a few differences between a sidechain and a mainchain, and because they viewm similar, people sometimes get them confused. Here are the main ways they differ:
1. Security: The mainchain is highly secure and fully decentralized, making it the trusted ledger for core transactions. A sidechain may use diverse rules or consensus methods, so it doesn’t always offer the identical level of security.
2. Flexibility: Sidechains can try out new features without affecting the mainchain. The mainchain, on the other hand, stays stable and unchanging to protect all core transactions.
3. Transaction Speed: Sidechains often process transactions quicker, which assists reduce congestion. The mainchain prioritizes security over speed, so it can be sluggisher for large volumes.
4. Use Cases: Sidechains are perfect for testing new applications and handling high-volume transactions. Mainchains handle high-value operations and remain the backbone of the blockchain network.
The Mechanics Behind Sidechains and Mainchains
The mainchain and sidechains are separate but connected networks that work together to make blockchain systems more efficient. The mainchain handles all core transactions and ensures security and reliability. It prioritizes securety over speed, which is why it can become sluggisher when handling large volumes of transactions.
A sidechain runs alongside the mainchain and takes on specific tasks to assist keep the network running smoothly. It can process transactions quicker, test new features, and run specialized applications without affecting the mainchain’s stability.
Assets can move between the two chains securely. When a token is sent to the sidechain, it is locked on the mainchain and unlocked on the supporting chain. When it returns, the process is reversed. This ensures that the total supply remains consistent and secure. Using auxiliary chains this way allows to scale efficiently, handle higher transaction volumes, and experiment with new protocols without putting the mainchain at risk. However, sidechains may not always offer the identical level of security as the mainchain, so careful management is required to prevent mistakes and potential threats.
Conclusion
Sidechains and mainchains each play a unique role in the blockchain ecosystem. Understanding how they complement each other assists you appreciate how blockchain networks can remain secure while still evolving and scaling. Mastering the balance between speed and security is key to building and using blockchain technology effectively.